Multiplex Sequencing
Processing more samples in less time
Increase the number of samples sequenced per run and optimize high-throughput sequencing
Sample Multiplexing Overview
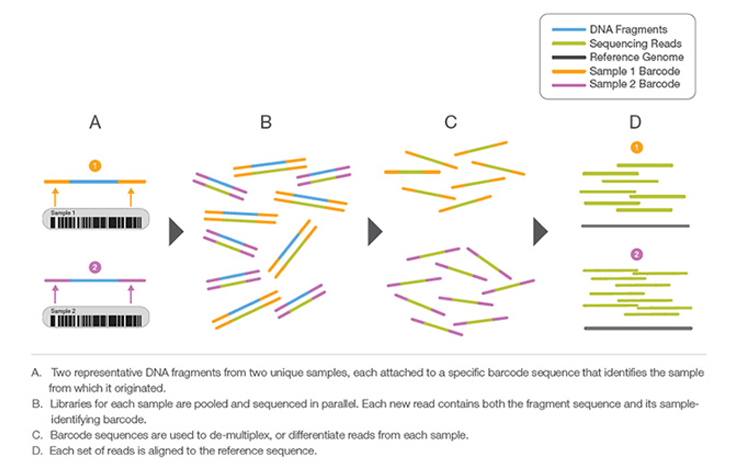
Sample multiplexing, also known as multiplex sequencing, allows large numbers of libraries to be pooled and sequenced simultaneously during a single run on Illumina instruments. Sample multiplexing is useful when targeting specific genomic regions or working with smaller genomes. Pooling samples exponentially increases the number of samples analyzed in a single run, without drastically increasing cost or time.
With multiplex sequencing, individual "barcode" sequences are added to each DNA fragment during next-generation sequencing (NGS) library preparation so that each read can be identified and sorted before the final data analysis. These barcodes, or index adapters, can follow one of two major indexing strategies depending on your library prep kit and application.
Multiplex Sequencing Highlights
- Fast high-throughput strategy: Large sample numbers can be simultaneously sequenced during a single experiment
- Cost-effective method: Sample pooling improves productivity by reducing time and reagent use
- Simplified analysis: Automatic sample identification with "barcodes" using Illumina data analysis software
Sample Multiplexing Facilitates Microbial Studies
Researchers leverage the speed and multiplex sequencing capabilities of Illumina sequencers to identify microbes along the Mississippi River.
Read InterviewRelated Topics in Multiplex Sequencing
Dual Index Sequencing
When preparing libraries for multiplexing, we recommend using unique dual indexes. Unique dual indexes allow you to increase the number of samples sequenced per run and reduce per-sample cost compared to other indexing strategies.
Learn MoreUnique Molecular Identifiers
Unique molecular identifiers (UMIs) are a type of molecular barcoding that provides error correction and increased accuracy during sequencing. Sequencing with UMIs can reduce the rate of false-positive variant calls and increase sensitivity of variant detection.
Learn MoreMinimizing Index Hopping
With multiplexing, the potential for index hopping is present regardless of the library prep method or sequencing system used. Learn best practices to help minimize the effects of index hopping.
Learn MoreChan Zuckerberg Biohub and the NovaSeq System
Researchers at the Chan Zuckerberg Biohub are working to conduct innovative experiments and form new collaborations in genomics. The NovaSeq System enables them to bundle many samples together for medical research that may help to improve human health.
View Video
Related Content
- High-Throughput Sequencing Methods: Cost-effectively run emerging data-rich methods, including single-cell and spatial analyses, and process more samples to improve statistical power.
- Library Prep Automation: Learn about automated liquid handling solutions designed to help labs prepare large quantities of sequencing libraries.
- Pooling Calculator: Dilute pooled libraries to the appropriate concentration for multiplex sequencing.
- Earlier QC metrics with index-first sequencing: This technical note demonstrates how index-first sequencing using the MiSeq i100 enables faster demultiplexing and real-time run management while providing high-quality data equivalent to read-first sequencing.
Interested in receiving newsletters, case studies, and information from Illumina based on your area of interest?
Sign up now.
Related Solutions
Library Prep and Array Kit Selector
Find the right sequencing library preparation kit or microarray for your needs. Filter by method, species, and more. Compare, share, and order kits.
Sequencing
Illumina sequencing allows researchers to ask virtually any question related to the genome, transcriptome, or epigenome of any organism.
Illumina sequencing platforms
View benchtop and production-scale sequencers and find resources designed to help you choose the right platform.