De Novo Sequencing
What Is De Novo Sequencing?
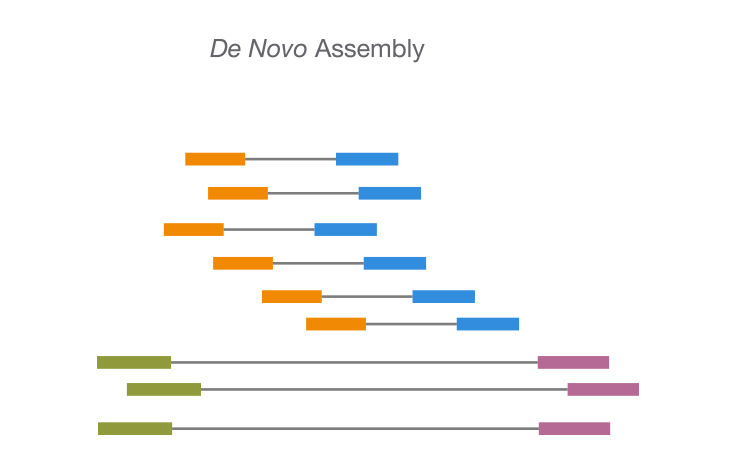
De novo sequencing refers to sequencing a novel genome where there is no reference sequence available for alignment. Sequence reads are assembled as contigs, and the coverage quality of de novo sequence data depends on the size and continuity of the contigs (ie, the number of gaps in the data).
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) allows faster, more accurate characterization of any species compared to traditional methods, such as Sanger sequencing. Illumina NGS technology offers rapid, comprehensive, accurate characterization of any species.
De Novo Sequencing in 3 Steps
Assemble novel bacterial genomes with this simple workflow solution.
Advantages of De Novo Sequencing
- Generates accurate reference sequences, even for complex or polyploid genomes
- Provides useful information for mapping genomes of novel organisms or finishing genomes of known organisms
- Clarifies highly similar or repetitive regions for accurate de novo assembly
- Identifies structural variants and complex rearrangements, such as deletions, inversions, or translocations

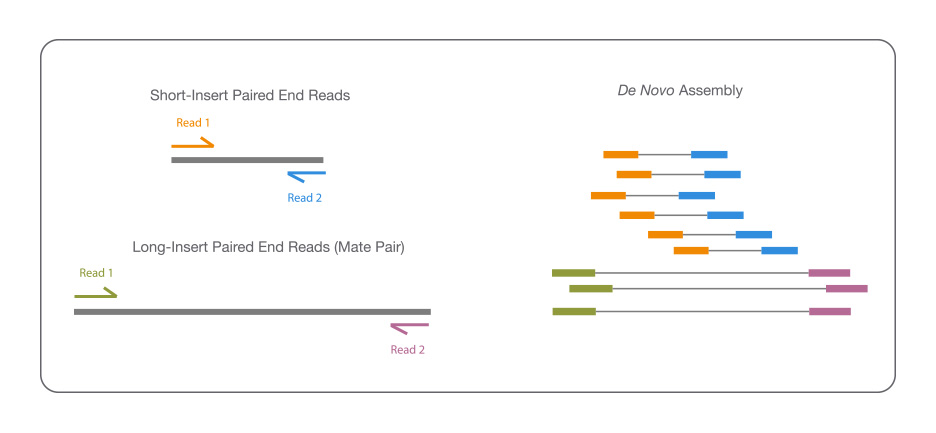
Accurate De Novo Genome Assembly
When sequencing a genome for the first time, a combined approach can yield higher-quality assemblies. For example, combining short-insert, paired-end and long-insert, mate pair sequences is one option to maximize coverage. The short reads, sequenced at higher depths, can fill in gaps not covered by the long inserts.
This combination enables detection of a broad range of structural variant types and is essential for accurate identification of complex rearrangements.
Featured De Novo Sequencing Articles
Illumina Sequencers Help Characterize and Control Coronavirus
See how Illumina NGS was used for de novo sequencing and characterization of the novel coronavirus genome, in combination with other technologies, as published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Read Article
Identifying Sweet Potato Viruses
Scientists at the Agricultural Research Council in South Africa use sequencing to identify known and novel sweet potato viruses, with the goal of enhancing food security.
Read Article
Advancing Species Research
Researchers at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology use de novo sequencing and other NGS methods to identify, characterize, and catalog the diversity of species on land and in the sea.
Read ArticleInvestigating the Genetics of COVID-19 Susceptibility
Illumina is providing sequencing for a UK-wide study led by Genomics England, designed to compare the genomes of severely and mildly ill COVID-19 patients. This research may help uncover genetic factors associated with susceptibility.
Read Article
Recommended Workflow for De Novo Bacterial Sequencing
Library Prep
Illumina DNA PCR-Free Prep
Exceptional ease-of-use, uniform coverage, and high-accuracy data for de novo microbial genome assembly.
Data Analysis
DRAGEN Bio-IT Platform
Provides accurate, ultra-rapid mapping, de novo assembly, and analysis of sequencing data.
Comprehensive De Novo Genome Sequencing Workflow
Illumina sequencing by synthesis (SBS) chemistry is the most widely adopted NGS technology, generating approximately 90% of global sequencing data.*
In addition to our industry-leading data quality, Illumina offers integrated workflows that simplify de novo sequencing, from library preparation to data analysis.
Click on the below to view products for each workflow step.
Exceptional ease-of-use, uniform coverage, and high-accuracy data for sensitive applications such as human WGS, de novo microbial genome assembly, and tumor–normal variant calling.
Learn more about long-read technology and explore partnership offerings ranging from de novo assembly services to genome phasing and structural variant detection.
Fast, user-friendly, affordable sequencing that provides uniform coverage and genome assembly for microbial species.
MiSeq SystemSpeed and simplicity for targeted and small genome sequencing.
NovaSeq 6000 SystemScalable throughput and flexibility for virtually any genome, sequencing method, and scale of project.
Compare sequencing platforms and identify the best system for your lab and applications.
Sequencing ReagentsFind kits that include sequencing reagents, flow cells, and/or buffers tailored to each Illumina sequencing system.
De novo assembler suitable for single-cell and isolate genomes.
BaseSpace Velvet De Novo Assembly AppDe novo assembly of bacterial genomes using the Velvet assembler.
Integrative Genomics ViewerDisplays alignments and variants from multiple samples for performing complex variant analysis.
Performs ultra-rapid secondary analysis of NGS data.
BaseSpace Sequence HubThe Illumina genomics computing environment for NGS data analysis and management.
Related Solutions
Choosing an NGS Company

Seek out a best-in-class next-generation sequencing company with user-friendly bioinformatics tools and industry-leading support and service. See the evidence.
Microbial Sequencing
Microbial whole-genome sequencing is an important tool for mapping genomes of novel organisms, finishing genomes of known organisms, or comparing genomes across multiple samples. Learn more about microbial WGS.
Cancer Whole-Genome Sequencing
Whole-genome sequencing of tumor samples provides a comprehensive view of the unique mutations in cancer tissue, informing analysis of oncogenes, tumor suppressors, and other risk factors. Learn more about cancer WGS.
Metagenomics
Shotgun metagenomic sequencing enables microbiologists to evaluate bacterial diversity and study unculturable microorganisms that are otherwise difficult or impossible to analyze. Learn more about metagenomic sequencing.
Plant and Animal Sequencing

De novo sequencing can provide insight into a plant or animal’s functions and environmental interactions. Some researchers use the assembled genome to assign map positions and stack diverse breed information for subsequent SNP discovery. Learn more about plant and animal sequencing.
Interested in receiving newsletters, case studies, and information on genomic analysis techniques? Enter your email address.
Additional Resources

Assembling the Kiwi Genome
Dr. Diana Le Duc uses de novo sequencing to understand the evolution of the kiwi bird.
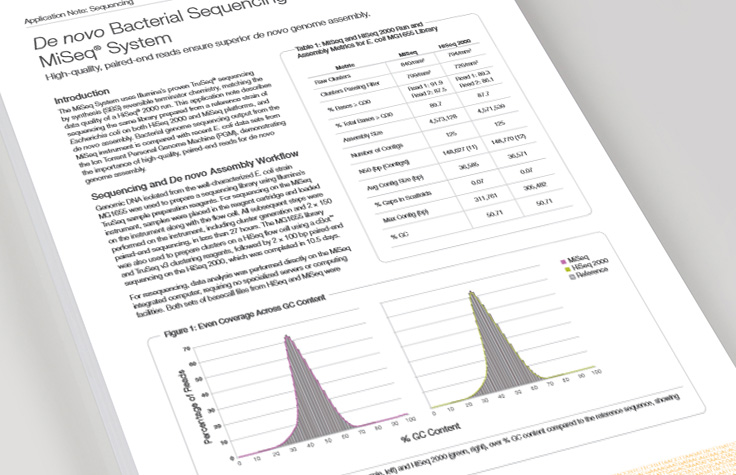
De Novo Bacterial Sequencing
The MiSeq System is an ideal platform for microbial genome sequencing and de novo assembly.
*Data calculations on file. Illumina, Inc., 2015