Large Whole-Genome Sequencing
Introduction to Large Whole-Genome Sequencing
Sequencing large genomes (> 5 Mb) can provide valuable information for disease and population-level studies. Researchers often use large whole-genome sequencing to analyze tumors, investigate causes of disease, select plants and animals for agricultural breeding programs, and identify common genetic variations among populations.
Large Whole-Genome Sequencing in 3 Steps
Obtain a base-by-base view of genomic alterations with this simple workflow solution.
Advantages of Large Whole-Genome Sequencing
- Provides a high-resolution, base-by-base view of the genome
- Combines short inserts and longer reads to allow characterization of any genome
- Reveals disease-causing alleles that might not have been identified otherwise
- Identifies potential causative variants for further follow-on studies of gene expression and regulation mechanisms
A Comprehensive View of Genetic Variation
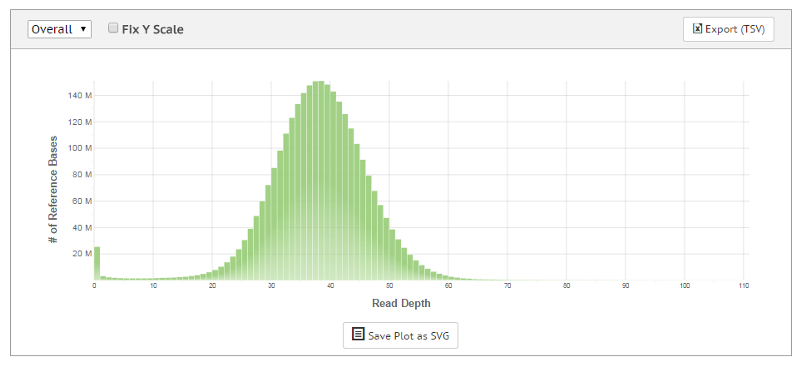
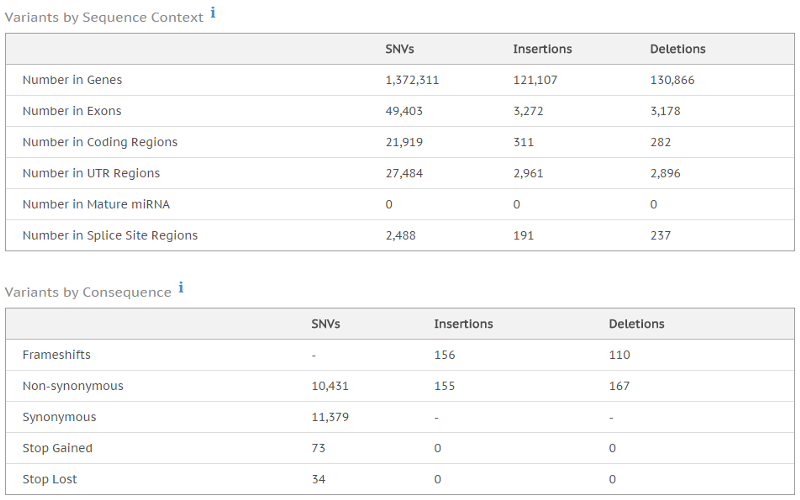
Analyzing the whole genome using next-generation sequencing (NGS) delivers a base-by-base view of all genomic alterations, including single nucleotide variants (SNV), insertions and deletions, copy number changes, and structural variations. Paired-end whole-genome sequencing involves sequencing both ends of a DNA fragment, which increases the likelihood of alignment to the reference and facilitates detection of genomic rearrangements, repetitive sequences, and gene fusions.
Featured Large WGS Research

Investigating the Genetics of COVID-19 Susceptibility
Illumina is providing sequencing for a UK-wide study led by Genomics England, designed to compare the genomes of severely and mildly ill COVID-19 patients.
Read Article
Searching for Cancer Driver Gene Expression Clues
WGS allows researchers to examine nucleosome patterns and infer the gene expression status of cancer driver genes in cell-free DNA.
Read Interview
Advancing Species Research
Researchers at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology use de novo WGS and other NGS methods to identify, characterize, and catalog the diversity of species on land and in the sea.
Read InterviewRecommended Workflow for Large Whole-Genome Sequencing
Library Prep
Illumina DNA Prep
A fast, integrated workflow for a wide range of applications, from human whole-genome sequencing to amplicons, plasmids, and microbial species.
Sequencing
NovaSeq 6000 System
Scalable throughput and flexibility for virtually any genome, sequencing method, and scale of project.
NovaSeq X
Extraordinary throughput and accuracy to perform data-intensive applications at production scale.
Data Analysis
Illumina DRAGEN Bio-IT Platform
Accurate, ultra-rapid analysis of sequencing data from whole genomes, with apps for analysis of germline and somatic datasets. Available on-premise or in BaseSpace Sequence Hub.
Comprehensive Large Genome Sequencing Workflow
Illumina sequencing by synthesis (SBS) chemistry is the most widely adopted NGS technology, generating approximately 90% of global sequencing data.*
In addition to our industry-leading data quality, Illumina offers integrated workflows that simplify the entire process, from library preparation to data analysis.
Click on the below to view products for each workflow step.
A fast, integrated workflow for a wide range of applications, from human whole-genome sequencing to amplicons, plasmids, and microbial species.
Illumina DNA PCR-Free PrepA high-performing, fast, and integrated workflow for sensitive applications such as human whole-genome sequencing.
Efficient library preparation from samples with limited available DNA, delivering high coverage quality and reduced bias.
Library Prep Kit SelectorDetermine the best kit for your needs.
Illumina Complete Long Read Prep, HumanDesigned for human whole-genome sequencing (WGS) by enabling short and long reads from a single platform.
Groundbreaking benchtop sequencers allow you to explore new discoveries across a variety of current and emerging applications.
NovaSeq 6000 SystemScalable throughput and flexibility for virtually any genome, sequencing method, and scale of project.
Compare sequencing platforms and identify the best system for your lab and applications.
Sequencing Reagents and Flow CellsFind kits that include sequencing reagents, flow cells, and/or buffers tailored to each Illumina sequencing system.
The Illumina DRAGEN (Dynamic Read Analysis for GENomics) Bio-IT Platform provides ultra-rapid secondary analysis of NGS data.
BaseSpace Sequence HubThe Illumina genomics computing environment for NGS data analysis and management.
BaseSpace Whole-Genome Sequencing AppQuickly extracts biological information from whole-genome sequences, using Isaac alignment and variant calling.
BaseSpace Tumor-Normal AppEnables researchers to detect somatic variants from a tumor and matched normal sample pair.
Associates single gene or list of genes with annotation data for pathways, diseases, tissues, and small molecules.
BaseSpace Correlation EngineA growing library of curated genomic data to support researchers in identifying disease mechanisms, drug targets, and biomarkers.
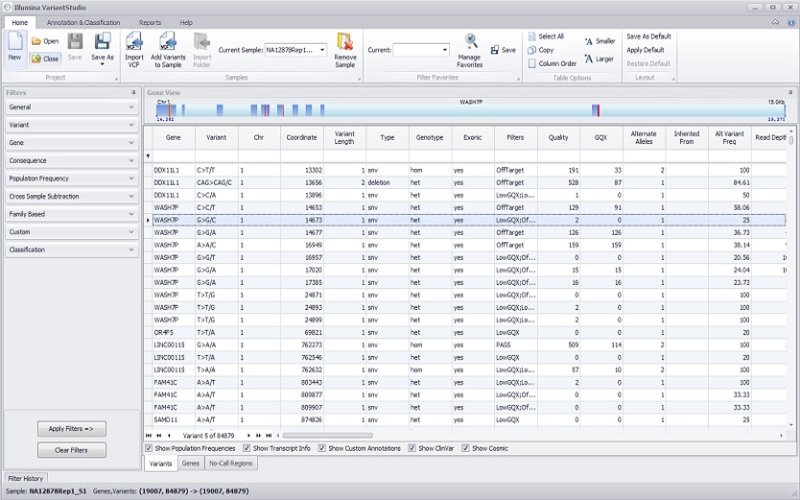
BaseSpace Variant InterpreterLeverages leading annotation databases and a powerful filtering interface to identify disease-associated variants rapidly.
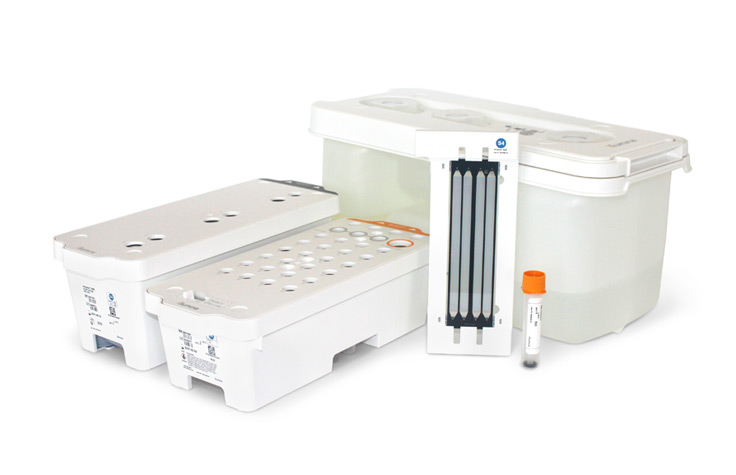

NovaSeq 6000 Flow Cell Options
Reagent kits for the NovaSeq 6000 System are available in multiple flow cell configurations to support a broad range of applications. SP and S1 are ideal for small batch sizes or in situations where rapid turnaround time is required. S2 is a quick, powerful, and cost-effective option for high-throughput applications. S4 offers ultra-high throughput sequencing across a wide range of sequencing methods.
View KitsRelated Solutions
Long-Read Sequencing Technology
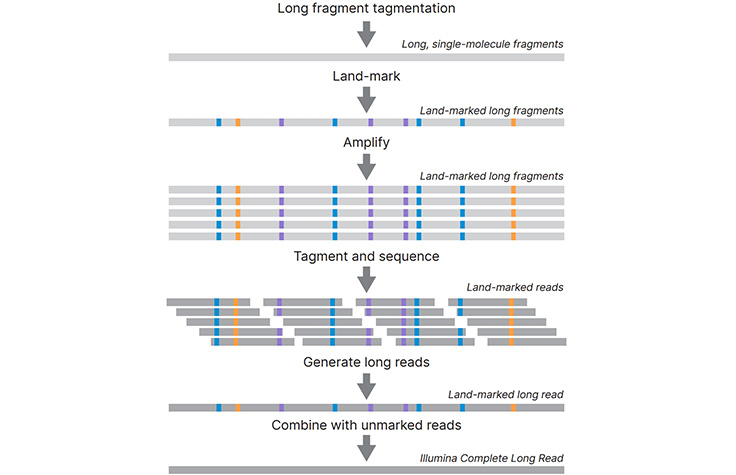
Long-read sequencing enables the sequencing of much longer DNA fragments than traditional short-read sequencing methods.
Complex Disease Research

Researchers can utilize WGS and other methods to identify genetic variants associated with complex diseases and characterize disease mechanisms.
Sequencing Cancer Genomes
Whole-genome sequencing of tumor and matched normal tissue samples provides a comprehensive view of the unique mutations in cancer, informing studies of oncogenes and other risk factors.
Causal Variant Studies
WGS can identify single nucleotide variants and copy number variations associated with diseases. Identifying these causal variants can help researchers characterize disease mechanisms.
Plant and Animal Sequencing

Whole-genome sequencing of plants and animals is an efficient approach for discovering genes, SNPs, and structural variants. This information can improve breeding and selection in agriculture.
Human Whole-Genome Sequencing

Previously a challenging application, human whole-genome sequencing has never been simpler. It offers the most detailed view into our genetic code.
Interested in receiving newsletters, case studies, and information on genomic analysis techniques? Enter your email address.
Additional resources

Human WGS on the NovaSeq 6000 System
See our best practices for generating high-quality data from human whole-genome sequencing on the NovaSeq 6000 System.

Sequencing to Understand Age-Related Diseases
Human Longevity, Inc. aims to address challenges related to aging and disease through the power of population genomics.
Paired-end sequencing facilitates detection of genomic rearrangements and repetitive sequence elements.

Modern Breeding Programs for Sunflower Farming
The sunflower industry adopts genomics tools to better inform breeding decisions and improve disease resistance.

Feline Social Media Star Gets Sequenced
Researchers crowdfunded the genome sequencing of Lil Bub to uncover the genetic causes of the cat's rare diseases.

NGS to Study Genetics of Brain Development
Researchers apply functional genomic methods to identify the role of gene variants in intellectual disability.

Shared Vision for the Power of Human WGS
Genomics leaders share their perspective on the impact of high-throughput and population sequencing in clinical research.
*Data calculations on file. Illumina, Inc., 2015